Regardless of whether duplicate content on a website is accidental or the result of someone stealing blocks of text from your web pages, it must be treated and handled correctly.
It doesn’t matter if you run a website for a small business or a large corporation; Every site is vulnerable to the threat that duplicate content poses to SEO rankings.
In this article, I’ll explain how to find duplicate content, how to determine if it’s affecting you internally or on other domains, and how to properly manage duplicate content issues.
What Constitutes Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content refers to blocks of content that are completely identical to each other (exact duplicates) or very similar, also known as common duplicates or near duplicates. Near duplicate content refers to two pieces of content with only minor differences.
Of course, having similar content is natural and sometimes unavoidable (i.e. quoting another article on the internet).
The Different Types of Duplicate Content
There are two types of duplicate content:
Duplicate internal content is when a domain creates duplicate content through multiple internal URLs (on the same website).
Duplicate external content, also known as cross-domain duplicates, occurs when two or more different domains have the same copy of the page indexed by search engines.
Both external and internal duplicate content can appear as exact duplicates or near duplicates.
Is Duplicate Content Bad For SEO?
Officially, Google does not impose any penalties for duplicate content. However, it filters identical content, which has the same impact as a penalty: the loss of ranking on your web pages.
Duplicate content confuses Google and forces the search engine to choose on which identical pages it should rank high. Regardless of who produced the content, there is a high possibility that the original page will not be chosen for the main search results.
This is just one of the many reasons why duplicate content is bad for SEO. Here are some other obvious reasons why duplicate content sucks.
Internal Duplicate Content Issues
On-Page Elements
To avoid duplicate content issues, make sure every page on your site has:
- A unique page title and meta description in the page’s HTML code
- headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) that differ from other pages on your site
The page title, meta description, and headings make up a minimum amount of content on a page. However, it is safer to keep your site out of the gray area of duplicate content as much as possible. It’s also a great way for search engines to see the value in your meta descriptions.
If you can’t write a unique meta description for each page because it has too many pages, delete it. Most of the time, Google takes snippets of your content and presents it as a meta description anyway. However, it is best to write a custom meta description, if possible, as it is critical to generating clicks.
Product descriptions
It is understandable that creating unique product descriptions is a challenge for many ecommerce businesses, as it can take a long time to write original descriptions for each product on a website.
However, if you want to rank for “Rickenbacker 4003 Electric Bass Guitar,”, you need to differentiate your product page for Rickenbacker 4003 from all other sites that offer this product.
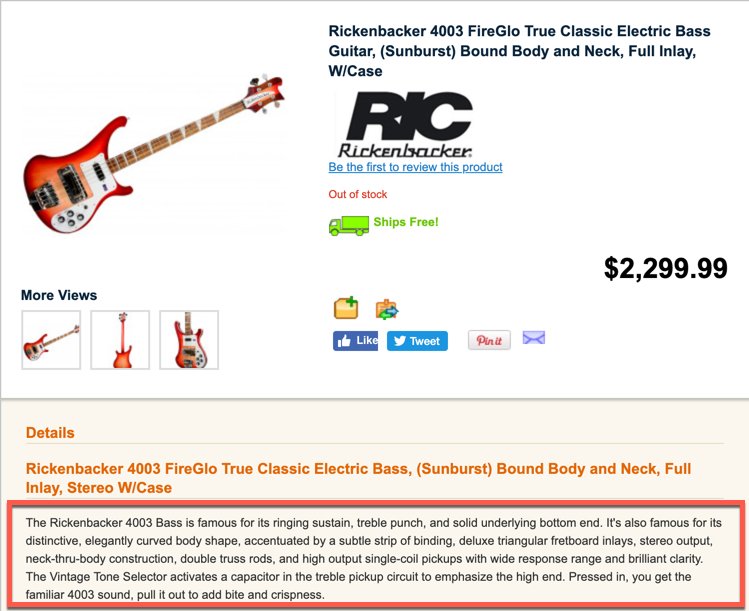
If you sell your products through third-party retail websites or have other resellers offering your product, please provide each source with a unique description.
If you want your product description page to outperform others, check out our article on how to write a great product description page.
Ideally, product variations such as size or color should not be on separate pages. Use web design elements to keep all variations of a product on one page.
URL Parameters
Another common problem with duplicate content found on e-commerce sites (although not unique to e-commerce) comes from URL parameters.
Some sites use URL parameters to create page URL variations (for example, ?sku=5136840, &primary-color=blue, &sort=popular), which can lead to search engines indexing different versions of the pages. URL, including parameters.
If your site uses URL parameters, see Portent CEO Ian Lurie’s article on URL parameter duplication, entitled The Duplication Toilet Bowl of Death.
WWW, HTTP, and The Trailing Slash
One area of duplicate internal content that is often overlooked is URLs with:
- www (http://www.example.com) and without www (http://example.com)
- http (http://www.example.com) and HTTPS (https://www.example.com)
- a slash at the end of a URL (http://www.example.com/) and without a trailing slash (http://www.example.com)
A quick way to check for these issues is to take a single text section from your most valuable landing pages, enclose the text in quotation marks, and Google it. Then Google will search for that exact text string. If more than one page appears in the search results, you will have to look closely to determine why this is happening, first by examining the possibility of the three options listed above.
If you discover that your site has a www vs. no www or trailing slashes vs. non-trailing slashes, you will need to configure a 301 redirect from the non-preferred version to the preferred version.
Note: There is no SEO benefit to whether or not you use www or the trailing slash in your URLs, it is a matter of personal preference.
External Duplicate Content Issues
If you have a significant amount of valuable content, it will most likely be republished on another site. As flattering as it is, you will have to do without it. These are the different ways that duplicate content occurs externally:
Scraped Content
Scraped Content is when a website owner steals content from another website in an attempt to increase the organic visibility of their website. Webmasters who copy content can also try to get machines to “rewrite” the copied content they stole.
Scraped Content can sometimes be easy to identify, as scrapers sometimes don’t bother to replace brand terms throughout the content.
How the manual action penalty works: A human Google reviewer will review the site to determine if a page meets Google’s Webmaster Quality Guidelines. If you are flagged for trying to manipulate Google’s search index, you will find that your site has been ranked significantly lower or completely removed from search results.
If you are a victim of copied content, you should report it to Google by reporting web spam under the “Copyright and other legal issues” option.
Syndicated Content
Content syndication is when another site republishes your content, which likely originally appeared on your blog. It is not the same as copying your content because it is something that you have offered to share elsewhere.
As crazy as it sounds, distributing your content has an advantage. This makes your content more visible, which can drive more traffic to your site. In other words, you are exchanging content and possibly search engine rankings for links to your site.
How to Check for Duplicate Content
If you have web pages with content that falls in search engine rankings, then you should check if your content has been copied and used on another website. Here are some ways to do this:
Exact-Match Search
Copy some text phrases from one of your web pages, enclose them in quotation marks, and search Google. By using quotes, you are telling Google that you want results that return the exact text. If multiple results appear, it means that someone has copied your content.
Copyscape
Copyscape is a free tool that checks the text on your web page for duplicate content found on other domains. If the text on your page has been scraped, the offending URL will appear in the results.
You vs. Duplicate Content
Let’s be honest; you didn’t go so far in producing original content that someone would steal your work and top it in search results.
The growing threat of duplicate content may seem overwhelming and will likely take a long time to address, but the work that goes into managing that content will be worth the return on investment.
By following the advice given and taking duplicate content management seriously, you will improve your ranking and ward off scrapers, thieves, and clueless newbies.
